Chapter 11. Gossip and the Channel Graph
In this chapter we will describe the Lightning Network’s gossip protocol and how it is used by nodes to construct and maintain a channel graph. We will also review the DNS bootstrap mechanism used to find peers to “gossip” with.
The “Routing fees and Gossip relaying” section is highlighted by an outline spanning the routing layer and peer-to-peer layer of Figure 11-1.
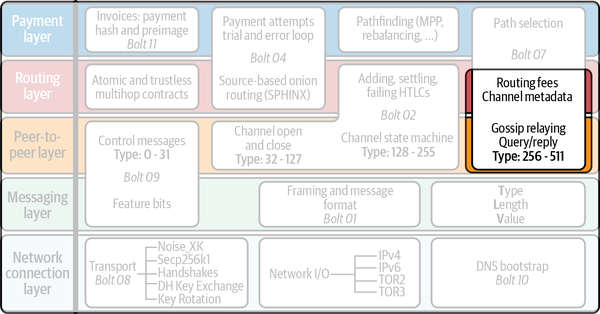
Figure 11-1. Gossip protocol in the Lightning protocol suite
As we’ve learned already, the Lightning Network uses a source-based onion routing protocol to deliver a payment from a sender to the recipient. To do this, the sending node must be able to construct a path of payment channels that connects it with the recipient, as we will see in Chapter 12. Thus, the sender has to be able to map the Lightning Network by constructing a channel graph. The channel graph is the interconnected set of publicly advertised channels and the nodes that these channels interlink.
As channels are backed by a funding transaction that is happening on-chain, one might falsely believe that Lightning nodes could just extract the existing channels from the Bitcoin blockchain. However this is only possible to a certain extent. The funding transactions are Pay-to-Witness-Script-Hash (P2WSH) addresses, and the nature of the script (a 2-of-2 multisig) will only be revealed once the funding transaction ...
Get Mastering the Lightning Network now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

