1.1 Communication System-on-Chip
1.1.1 Introduction
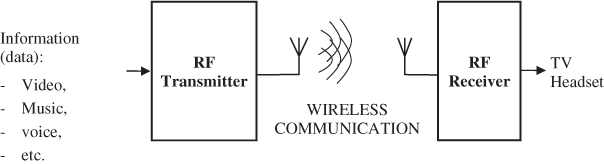
Radio frequency (RF) communication systems use RFs to transmit and receive information such as voice and music with FM, or video with TV, and so on (Steele, 1995; Rappaport, 1996; Haykin, 2001). From a general point of view RF communication is simply composed of an RF transmitter sending the information and an RF receiver recovering the information (Figure 1.1). Below are basic definitions of the vocabulary commonly used in communication systems:
- Signal: Information (data, image, music, voice, …) we want to transmit and receive.
- Carrier frequency: RF sinusoidal waveform, called a carrier because it is used to “carry” the signal from the transmitter to the receiver.
- MODulation: Modifying the carrier waveform in order to convey the information (signal) in transmission.
- DEModulation: Extracting the signal (i.e., the information) from the carrier frequency in reception.
- Antenna: Device which transforms the electrical signal into electromagnetic waves for radiation and vice versa.
- Channel bandwidth: Span of frequencies used for the communication.
- MODEM = MODulator + DEModulator.
- TRANSCEIVER = TRANSmitter + reCEIVER.
Figure 1.1 Basic view of an RF communication system
In the last decades telecommunications have migrated toward digital technology (Proakis, 1995) as a result of the evolution of advanced digital signal processing (DSP) ...
Get RF Analog Impairments Modeling for Communication Systems Simulation: Application to OFDM-based Transceivers now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

