
Feedback is a topic of paramount importance in analog design. It is a key concept that enables us to construct almost ideal analog circuits from the poorly controlled and very nonideal transistors readily available to us. By doing so, it facilitates the division of complex systems into smaller subblocks that may be designed independently.
5.1 IDEAL MODEL OF NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
We begin by considering the simplified model of a very general negative feedback system in Fig. 5.1. Its analysis finds overlap in introductory control theory and is applicable to a wide variety of systems, including analog integrated circuits. Later in this chapter, we refine our analysis making it progressively better suited to the circuits of most interest to us.
5.1.1 Basic Definitions
The linear time-invariant negative feedback system in Fig. 5.1 includes an amplifier, A, and some feedback circuitry whose gain is ß. Also labelled in Fig. 5.1 are the input signal, u, the output signal, y, the feedback signal, v, and the difference signal,
![]()
Physically, each of these signals may be small-signal node voltages or branch currents.1
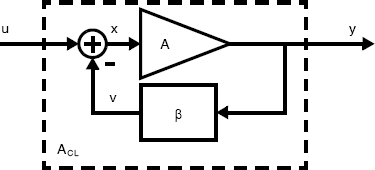
Fig. 5.1 Ideal model of a negative feedback
Clearly,
where we have defined ...
Get Analog Integrated Circuit Design, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

