Orientation
You start with an optional orientation—either H: for horizontal or V: for vertical alignment. This specifies whether the constraint applies left and right or up and down. If omitted, the orientation defaults to horizontal. Consider this constraint: "H:[view1][view2]". It says to place View 2 directly to the right of View 1. The H specifies the alignment that the constraint follows. Figure 5-2 (left) shows an interface that uses this rule.
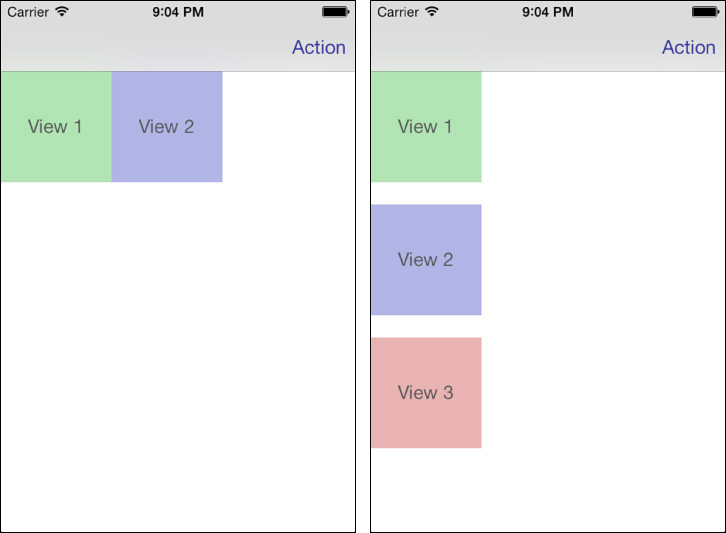
Figure 5-2 Layout results for "H:[view1][view2]" (left) and "V:|[view1]-20-[view2]-20-[view3]" (right).
The following is an example of a vertical layout: "V:|[view1]-20-[view2]-20-[view3]". It leaves ...
Get The Core iOS Developer’s Cookbook, Fifth Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

