Core message patterns: one message/two services
1/2: Request/Response
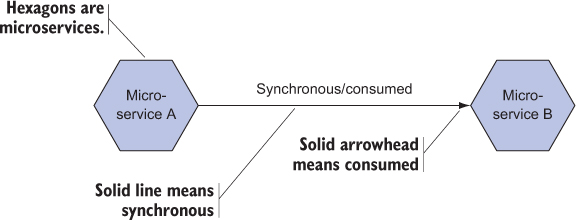
In this pattern, the message is synchronous. The sending microservice expects an immediate response. The message is also consumed, meaning that only one microservice generates a response to the message. This common case is analogous to the HTTP request/response model, with point-to-point communication between microservice instances.
Example: Sending a “command” message.
1/2: Sidewinder

The message is synchronous, with at least one immediate response expected. However, in ...
Get The Tao of Microservices now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

