XSL Formatting Objects
An XSL-FO document describes the layout of a series of nested rectangular areas (boxes, for short) that are placed on one or more pages. These boxes contain text or occasionally other items, such as an external image or a horizontal rule. There are four kinds of areas:
Block areas
Inline areas
Line areas
Glyph areas
Block and inline areas are created by particular elements in the
formatting objects document. Line and glyph areas are created by the
formatter as necessary. For the most part, the rendering engine
decides exactly where to place the areas and how big to make them
based on their contents. However, you can specify properties for these
areas that adjust both their relative and absolute position, spacing,
and size on a page. Most of the time, the individual areas don’t
overlap. However, they can be forced to do so by setting the
properties absolute-position,
left, bottom, right, and top.
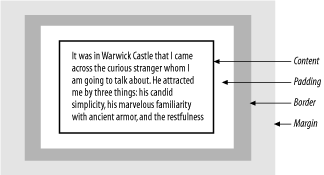
Considered by itself, each box has a content area in which its content, generally text but possibly an image or a rule, is placed. This content area is surrounded by a padding area of blank space. An optional border can surround the padding. The size of the area is the combined size of the border, padding, and content. The box may also have a margin that adds blank space outside the box’s area, as diagramed in Figure 14-1.