Chapter 20
VCO (Voltage-Controlled Oscillator)
20.1 “Three-Point” Types of Oscillator
There are many single-ended oscillators in RF circuit design. In this subsection, only the “three-point” type oscillators are discussed. Among the three-point type oscillators, the most popular one applied in communication systems is the Clapp oscillator, which will therefore be discussed in Section 20.1.3 in somewhat detail.
A three-point type oscillator contains only one device, either a bipolar transistor or a MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor). The AC equivalents of these three points are the base, collector, and emitter for a bipolar transistor, or the gate, drain, and source for a MOSFET. Figure 20.1 shows the AC equivalent of a three-point oscillator built by a MOSFET. The three nodes marked with 1, 2, and 3, are connected to the gate, drain, and source of the MOSFET, respectively. On the other hand, the three parts with impedances Z1, Z2, and Z3 are connected between nodes 1 and 3, 3 and 2, and 2 and 1, respectively.
Figure 20.1 AC equivalent of a three-point type of oscillator. (a) Tank circuit in input side. (b) Tank circuit in output side. (c) Tank circuit in both of input and output side.
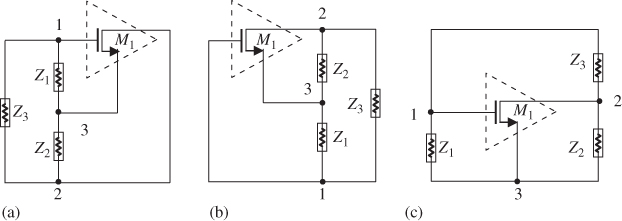
These three parts form a tank circuit loop. The AC equivalents plotted in Figure 20.1(a)–(c) are exactly the same circuit. The only difference between Figure 20.1(a), (b), ...
Get RF Circuit Design, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

