EPS Key Hierarchy
Two requirements bound the EPS key hierarchy and derivation. The first is that the EPC and E-UTRAN shall allow for use of encryption and integrity protection algorithms for AS and NAS protection having keys of length 128 and for future use the network interfaces shall be prepared to support 256 bit keys. The second is that keys for the user plane, NAS and AS protection shall be dependent on the algorithm with which they are used.
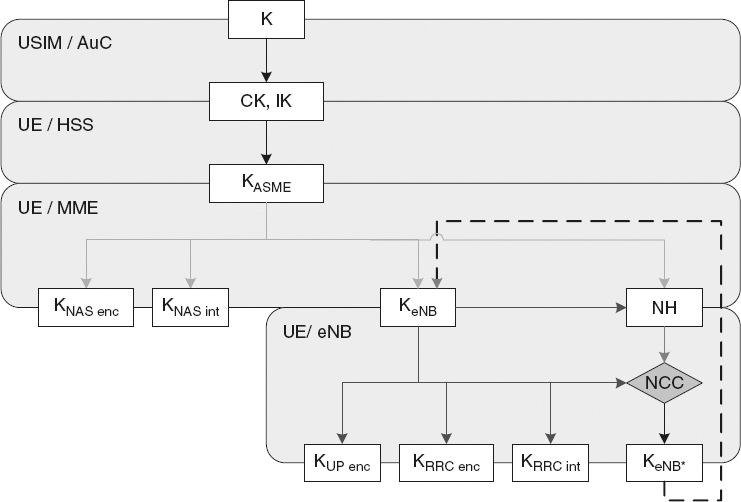
Figure 14.3 EPS Key Hierarchy and Derivation. Reproduced by permission of © 2010 3GPP. Further use is strictly prohibited.
The hierarchy, shown in Figure 14.3, includes the following keys: KeNB, KNASint, KNASenc, KUPenc, KRRCint and KRRCenc. A brief description of the different keys and how they are derived is provided below.
- KeNB is a key derived by UE and MME from KASME. KeNB may also be derived by the target eNB from NH at handover. KeNB shall be used for the derivation of KRRCint, KRRCenc and KUPenc, and for the derivation of KeNB* upon handover.
Keys for NAS traffic:
- KNASint is a key, which shall only be used for the protection of NAS traffic with a particular integrity algorithm. This key is derived by UE and MME from KASME, as well as an identifier for the integrity algorithm.
- KNASenc is a key, which shall only be used for the protection of NAS traffic with a particular encryption algorithm. This key is derived by UE and MME ...
Get LTE, LTE-Advanced and WiMAX: Towards IMT-Advanced Networks now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

