IEEE 802.16-2009
The IEEE 802.16 standard describes several modes of operation, each of which fits a specific deployment objective. In the amalgamated standard document, IEEE 802.16-2009, two modes are described: a mandatory Point-to-Multi-Point (PMP) and an optional Multihop Relay (MR). While both modes describe regular downlink communication, that is, from gateway or base station to mobile terminal, the MR mode utilizes intermediate RSs between a cell's BS and the MT. This latter is described in the amendment IEEE 802.16j. An example of an IEEE 802.16-2009 deployment is shown in Figure 3.1.
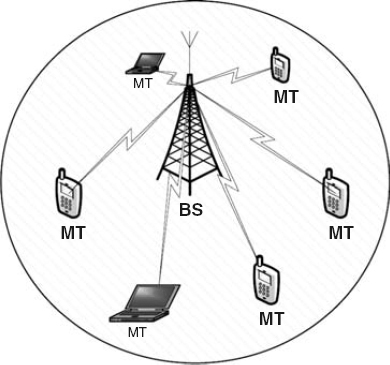
Figure 3.1 A schematic of a IEEE 802.16-2009 deployment, including a base station and different types of mobile terminals.
In a PMP deployment, BSs provide a continuous coverage through a cellular configuration, with the BSs interconnected through a network management infrastructure that oversees the overall management of network operations. Through the BSs, Subscriber Stations (SSs) and Mobile Subscribers (MSs) connect to the network and, when applicable, to the Internet. In the standard, the generic term SS describes user equipment capable of using different RITs operating under both, Line of Sight (LOS) and Non LOS (NLOS) circumstances. On the other hand, MSs are equipment sets whose connected mobility is supported in the NLOS network. As will be described below, mobility is supported only ...
Get LTE, LTE-Advanced and WiMAX: Towards IMT-Advanced Networks now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

