1.4 CATEGORIZATION OF OBSOLESCENCE MANAGEMENT APPROACHES
DMSMS require addressing the problem of obsolescence on three different management levels: reactive, proactive, and strategic, as shown in Figure 1-4.
FIGURE 1-4 Three obsolescence management DMSMS categories and the resulting outputs (adapted from Sandborn, 2008).
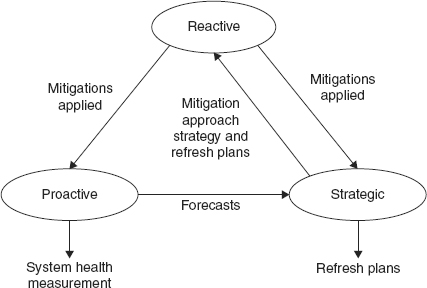
Reactive management (see Chapter 7) is concerned with determining an appropriate, immediate resolution to the problem of components becoming obsolete, executing the resolution process, and documenting/tracking the actions taken. Common reactive DMSMS management approaches include, among others, lifetime buy, bridge buy, component replacement, buying from aftermarket sources, uprating, emulation, and salvage (Sandborn, 2008).
Proactive management (see Chapter 8) is implemented for critical components that have a risk of going obsolete, lack sufficient available quantity after obsolescence, and will be problematic to manage if or when they become obsolete. These critical components are identified and managed prior to their actual obsolescence event. Bill of material (BOM) management regarding obsolete or soon to be obsolete components is an important part of the design and manufacture of any product. Proactive management requires the ability to forecast obsolescence risk for components. It also requires there be a process for articulating, reviewing, and updating ...
Get Strategies to the Prediction, Mitigation and Management of Product Obsolescence now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

