DHCP Packet Structure
Let’s
examine the packet structure of the DHCP protocol. As you will see,
the DHCP packet structure is fundamentally the same as the BOOTP
packet structure. There are only two differences: the
vend field was changed to the
options field, and this field was expanded from 64
octets in length to a minimum of 312 octets.
As shown in Figure 3.1, a DHCP packet’s transmission order is from left to right, top to bottom. The number shown in parentheses is the number of octets (or bytes) each field occupies.
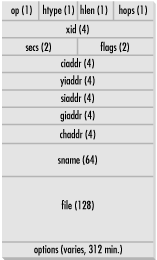
Figure 3-1. DHCP packet structure
Field Definitions
Table 3.1 lists the available fields in a DHCP packet and describes the type of information each field supplies.
Table 3-1. DHCP Field Definitions
|
Field |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the message type: if 1, the message is a BOOTPREQUEST; if 2, the message is a BOOTPREPLY. |
|
|
Specifies the hardware address type (i.e., ethernet or token ring). 10 Mbps Ethernet = 1. |
|
|
Specifies the hardware address length. Ethernet = 6. |
|
|
Specifies the number of hops between the client and the server. |
|
|
Specifies the transaction ID number. This is a random number that is used to match up the request with the reply that is returned. |
|
|
Specifies how long it has been since the client was booted. |
|
|
Specifies whether the BOOTPREPLY message should be sent as a unicast message or a broadcast message. ... |
Get DHCP for Windows 2000 now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

