socketpair 
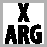


socketpairSOCKET1,SOCKET2,DOMAIN,TYPE,PROTOCOL
This function creates an unnamed pair of sockets in the
specified domain of the specified type.
DOMAIN, TYPE, and
PROTOCOL are specified the same as for
socketpair(2). You will need to use Socket to get the required constants. If
either socket argument is undefined, it will be autovivified. The
function returns true if successful, and false otherwise. On a system
where socketpair(2) is unimplemented, calling this
function raises an exception.
This function is typically used just before a fork. One of the resulting processes should
close SOCKET1, and the other should close
SOCKET2. You can use these sockets
bidirectionally, unlike the filehandles created by the pipe function. Some systems define pipe using socketpair, in which a call to pipe(Rdr, Wtr) is essentially:
use Socket; socketpair(Rdr, Wtr, AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, PF_UNSPEC); shutdown(Rdr, 1); # no more writing for reader shutdown(Wtr, 0); # no more reading for writer
Perl v5.8 and later will emulate socketpair using IP sockets to localhost if your system implements sockets ...