5.2 CLASSIFICATION OF INTERCONNECTION NETWORKS BY LOGICAL TOPOLOGIES
The interconnection network topology is usually drawn as a graph with nodes representing the switches or processors and the edges representing the communication links between the switches or processors. There are major well-known network topologies that are summarized in the following sections.
5.2.1 Bus
A bus is the simplest type of interconnection network as shown in Fig. 5.1. The shaded squares represent medium access control (MAC) controllers. These controllers could be simple arbiters or they could be ethernet controllers if the bus is an ethernet local area network (LAN). They could also represent wireless devices if the bus physical medium is a wireless channel.
Figure 5.1 A bus interconnection network. The shaded squares represent MAC controllers.
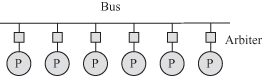
All processors and memory modules are connected to the bus, and communication between any pair of processors takes the same amount of time no matter how far apart they are. The bus, however, allows only one processor to access the shared medium at any given time so as to prevent bus access collisions. Each module connected to the bus is characterized by its own unique MAC address for identification. The source processor communicates with another processor or memory module by specifying the destination MAC address. Some form of MAC arbitration scheme must be ...
Get Algorithms and Parallel Computing now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

