15.3 OBTAINING THE ALGORITHM DEPENDENCE GRAPH
The string matching algorithm of Eq. 15.1 is defined on a two-dimensional (2-D) domain since there are two indices (i, j). Therefore, a data dependence graph can be easily drawn as shown in Fig. 15.1. The computation domain is the convex hull in the 2-D space where the algorithm operations are defined as indicated by the grayed circles in the 2-D plane [86]. The output variable y is represented by vertical lines so that each vertical line corresponds to a particular instance of y. For instance, the line described by the equation i = 3 represents the output variable instance y3. The input variable t is represented by the slanted lines. Again, as an example, the line represented by the equation
(15.2)
![]()
Figure 15.1 Dependence graph for m = 4 and n = 10.
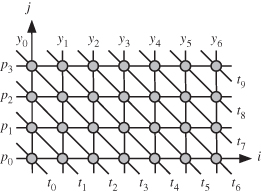
represents the input variable instance t3. Similarly, the input variable p is represented by the horizontal lines.
Get Algorithms and Parallel Computing now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

