PROBLEMS
3.1 Given the Poisson random variable with the discrete probability in Eq. (3.3.19), its jth moment is computed as
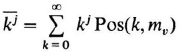
Determine the mean value, mean-square value, and variance of the Poisson variable.
3.2 The characteristic function Ψ(jω) of any discrete random variable is computed from its probability function P(k) as
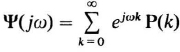
The moment generating function M(z) is obtained from Ψ(jω) by
replacing jω = in(1 − z). Show that
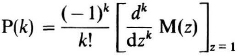
3.3 Use the results of Problem 3.2 to derive the Poisson count probability from its characteristic function.
3.4 Electrons are emitted from a photodetecting surface according to a Poisson probability with mean value m. Suppose, however, the probability that a given emitted electron will be collected at the output is η. Determine the resulting count probability of the electrons collected at the output. Hint: Treat the conversion of each emitted electron to an output electron as a binary random variable with probability η.
3.5 Let Wn be the time for n events to occur in a counting process k(t). The variable Wn is called the waiting time to the nth event. Show that if the events occur with a Poisson probability with mean rate ν events/second then
- (a)
- (b)
- (c)
- (d) ...
Get Optical Communications, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

