This is the Title of the Book, eMatter Edition
Copyright © 2007 O’Reilly & Associates, Inc. All rights reserved.
310
|
Chapter 13: Network Infrastructure for VoIP
practical. They might be needed in very demanding scenarios, such as a call center
with offices in multiple states or highly redundant military or intelligence
applications.
Quality-of-service measures must be more sophisticated when used in a highly-
meshed network. Indeed, one thing RSVP is designed to do is negotiate the best-
quality path through the network for a phone call when there are multiple potential
paths. This is quite different from dynamic routing alone, which chooses paths
across the network based on policies that have no direct relationship with the voice
application.
Layout and PBX Placement
Most networks employ a combination of distributed and client-server models for dif-
ferent applications and a combination of different layout techniques for different bal-
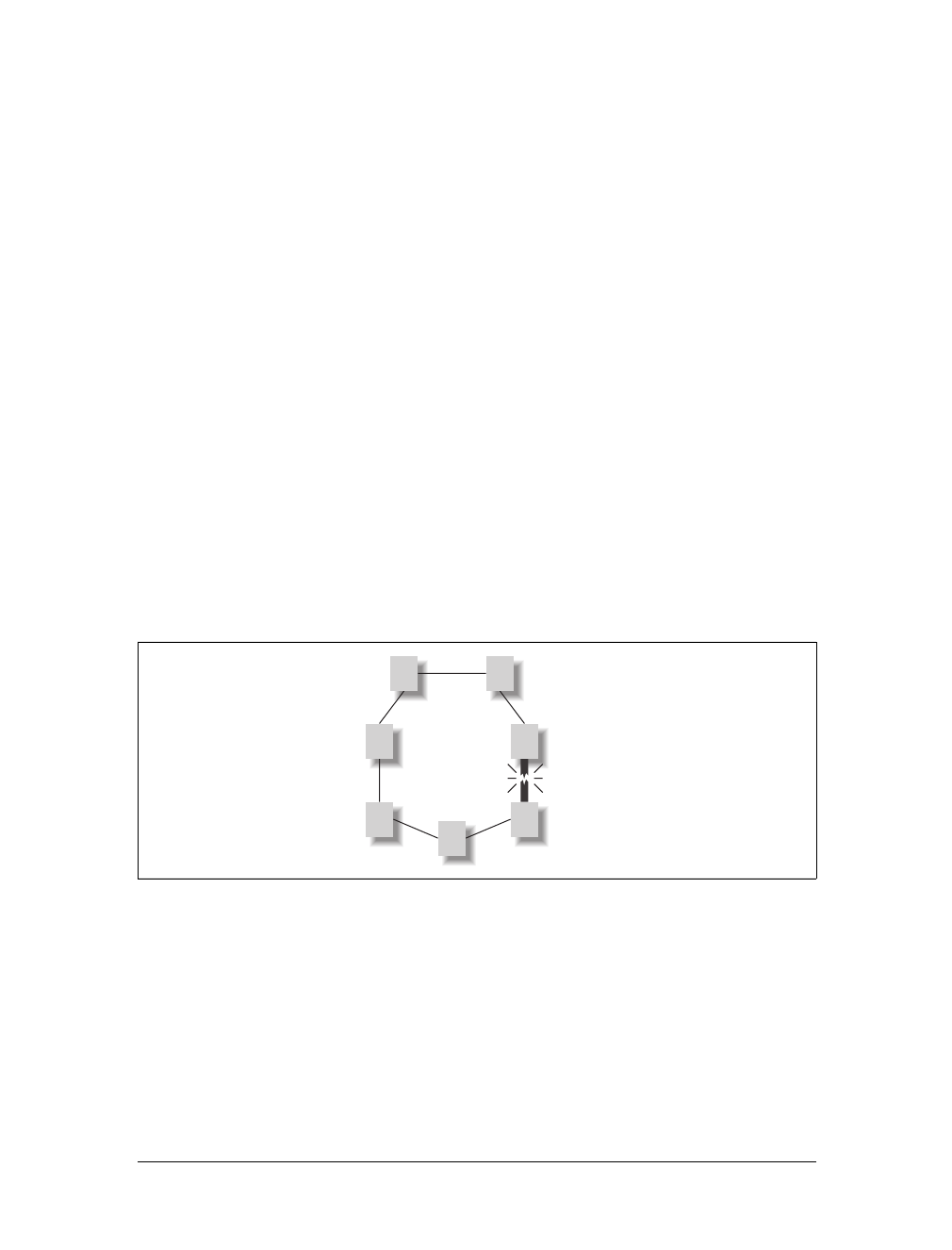
ances of cost and resilience to failure. As long as the total number of remote
locations is under 10 or so, a circular peer network is a great solution to the down-
time issue, because if an upstream route fails, the other arc of the circle is still up and
also leads back to the data center. This functionality is handled by—you guessed it—
IP routing. So it takes two points of failure on the circle in order to bring the voice
transport down for any one site, as
