3.8. Discovering the IMS entry point
In order to communicate with the IMS, an item of UE has to know at least one IP address of the P-CSCF. The mechanism by which the UE retrieves these addresses is called "P-CSCF discovery". Two dynamic mechanisms for P-CSCF discovery have been standardized in 3GPP: the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol's (DHCP) DNS procedure and the GPRS procedure. Additionally, it is possible to configure either the P-CSCF name or the IP address of the P-CSCF in the UE.
In the GPRS procedure (Figure 3.7), the UE includes the P-CSCF address request flag in the PDP context activation request (or secondary PDP context activation request) and receives the IP address(es) of the P-CSCF in the response. This information is transported in the protocol configuration options information element [3GPP TS 24.008]. The mechanism the Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) used to get the IP address(es) of the P-CSCF(s) is not standardized. This mechanism does not work with pre-Release 5 GGSNs.
Figure 3.7. A GPRS-specific mechanism for discovering the P-CSCF.
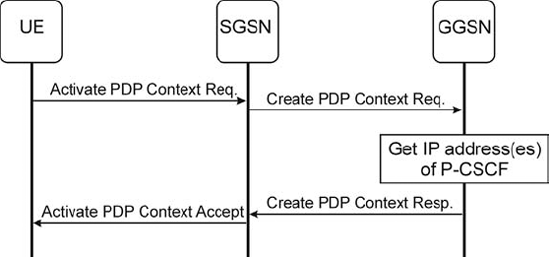
Figure 3.8. A generic mechanism for discovering the P-CSCF.
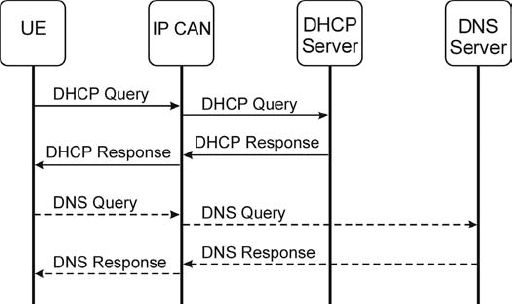
In the DHCP DNS procedure (Figure 3.8), the UE sends a DHCP query to the IP connectivity access network (e.g., GPRS), which relays the request to a DHCP server. ...
Get The IMS: IP Multimedia Concepts And Services, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

