5.5 Optimal Rate Allocation for H.264/AVC Joint MVS Transcoding
(Portions reprinted, with permission, from “Joint bit-allocation for multi-sequence H.264/AVC video coding rate control”, Picture Coding Symposium, Lisbon, November 2007. ©2007. EURASIP)
5.5.1 Problem Definition and Objectives
Let us consider the scenario depicted in Figure 5.5, where the input is represented by a set of pre-encoded H.264/AVC sequences, each encoded in either VBR or CBR mode. The sequences are multiplexed into a single channel, characterized by a global rate constraint Rtot. Therefore, the problem is twofold:
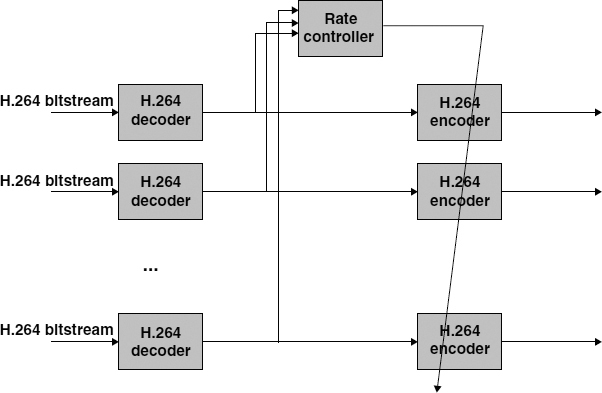
Figure 5.5 Proposed transcoding architecture for multi-sequence rate control. Reproduced by permission of ©2007 EURASIP
- The rate controller module is responsible for optimally allocating the bit budget to the output sequences.
- Transcoding needs to be performed in order to meet a more stringent rate constraint and adjust the output bit rate of the sequences.
In this work, the focus is on defining novel solutions for the rate control module, while a very simple transcoding algorithm is envisaged in order to serve as a “proof of concept”. Specifically, in order to avoid issues related to drift propagation, an explicit transcoder that decodes the sequence in the pixel domain and re-encodes it subject to the new, more stringent, rate constraint is adopted. In order to speed up the transcoding process, ...