Internet Protocol (IP) Addressing and Subnet Mask
The Internet Protocol address (IP address) is either a class "A," "B," or "C" address (there are also class "D" and "E" addresses I will not cover). A class “A” network supports many more nodes per network than either a class "B" or "C" network. IP addresses consist of four fields. The purpose of breaking down the IP address into four fields is to define a node (or host) address and a network address. Figure 12-3 summarizes the relationships between the classes and addresses.
Figure 12-3. Comparison of Internet Protocol (IP) Addresses
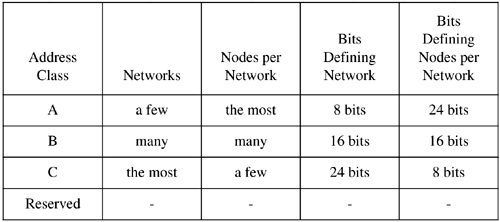
These bit patterns are significant in that the number of bits ...
Get HP-UX 11i System Administration Handbook and Toolkit, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

