THE TRADE LIFE CYCLE FOR CROSS-CURRENCY SWAPS
- Recording the trade—contingent
- Account for the upfront fee (premium on the trade)
- Pay/receive the upfront fee for the trade
- Reset the interest rate for both legs—receivable and payable
- Account for accrued interest on pay leg on valuation date
- Account for accrued interest on receive leg on valuation date
- Reverse the accrued interest on pay leg on coupon date
- Reverse the accrued interest on receive leg on coupon date
- Account for the interest payable on the pay leg on coupon date
- Account for the interest receivable on the receive leg on coupon date
- Pay the pay leg (one currency)
- Receive the receive leg (another currency)
- Reverse the existing net present value of the trade
- Ascertain the fair value on valuation date
- Termination of the trade and accounting for termination fee
- Payment or receipt of termination fee
- Maturity of the trade
- Reversal of the contingent entry on maturity/termination
- FX revaluation entries
- FX translation entries
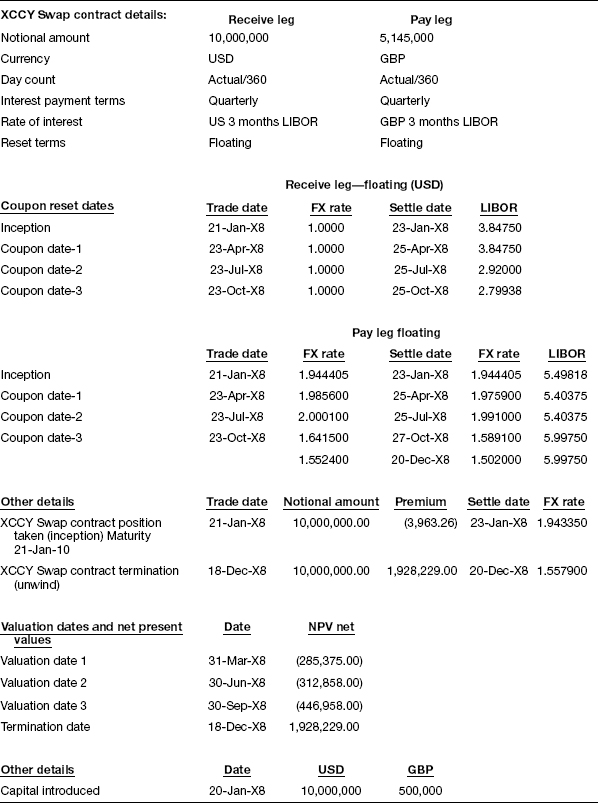
Let us assume the contract data as shown in Table 12.2 for the purpose of understanding the trade life cycle for a cross-currency interest rate swap.
Table 12.2 Details of cross-currency swap contract

Recording the trade—contingent
Unlike interest rate swaps there may be an exchange of principal taking place ...
Get Accounting for Investments, Volume 2: Fixed Income Securities and Interest Rate Derivatives—A Practitioner's Guide now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

