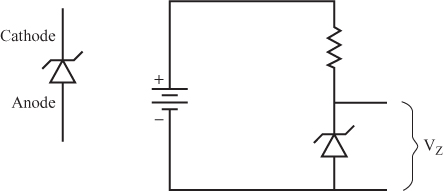
The Zener Diode
24 Diodes can be manufactured so that breakdown occurs at lower and more precise voltages than those just discussed. These types of diodes are called zener diodes, so named because they exhibit the “Zener effect”—a particular form of voltage breakdown. At the zener voltage, a small current flows through the zener diode. This current must be maintained to keep the diode at the zener point. In most cases, a few milliamperes are all that is required. Figure 2.26 shows the zener diode symbol and a simple circuit.
In this circuit, the battery determines the applied voltage. The zener diode determines the voltage drop (labeled Vz) across it. The resistor determines the current flow. Zeners are used to maintain a constant voltage at some point in a circuit.
Why are zeners used for this purpose, rather than ordinary diodes? _____
Because zeners have a precise breakdown voltage.
25 Examine an application in which a constant voltage is wanted—for example, a lamp driven by a DC generator. In this example, when the generator turns at full speed, it puts out 50 volts. When it runs more slowly, the voltage can drop to 35 volts. You want to illuminate a 20-volt lamp with this generator. Assume that the lamp draws 1.5 amperes. Figure 2.27 shows the circuit.
You need to determine a suitable value for the resistance. Follow these ...
Get Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with Projects now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.