1.4. Principal Findings from GEM
The total entrepreneurial activity (TEA) by country in 2009 is shown in Figure 1.2. The TEA varied from a low in Japan of 3.3% to a high in Uganda of 33.7% for adults 18 to 64 years old. The average level was 10.7% or 1 adult in 11.
Figure 1.2. Early-stage TEA for 54 nations in 2009
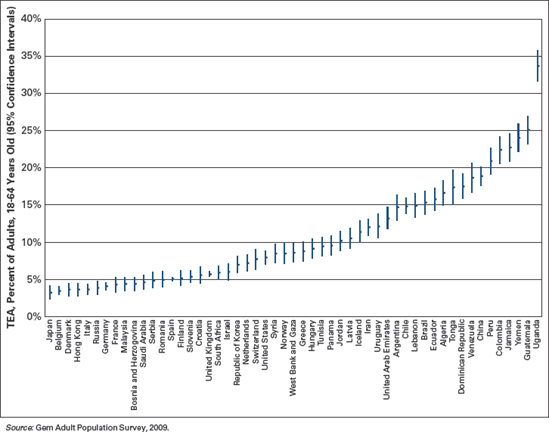
The vertical bars in Figure 1.2 are 95% confidence intervals. These error bars are wide for some countries and narrow for others because of different sample sizes. Germany, Spain, and the United Kingdom have narrow bars because the samples were very large. Where bars overlap there is no statistical difference among those nations. For example, among countries with lower TEA rates, Japan, Belgium, Denmark, Hong Kong, Italy, Russia, Germany, and France have comparable levels of entrepreneurial activity; among countries with more entrepreneurial activity, Colombia, Jamaica, Yemen, and Guatemala have comparable TEA rates.
GEM defines two types of entrepreneurship: opportunity based and necessity based. In general, nations with high per capita income have proportionately less necessity-pushed entrepreneurial activity and more opportunity-pulled entrepreneurial activity and vice versa for nations with low income, as shown in Figure 1.3. People in higher-income nations tend to have more opportunities for employment and stronger safety nets like social welfare programs, especially ...
Get Entrepreneurship, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

