May 2020
Beginner to intermediate
430 pages
10h 39m
English
Dropout is a special type of regularization and refers to ignoring neurons in the neural network. A fully connected layer with dropout = 0.2 means that only 80% of the fully connected neurons are connected to the next layer. The neurons are dropped at the current step but are active at the next step. Dropout prevents the network from being dependent on a small number of neurons, thus preventing overfitting. Dropout is applied to input neurons, but not the output neurons. The following diagram shows the neural network with and without dropout:
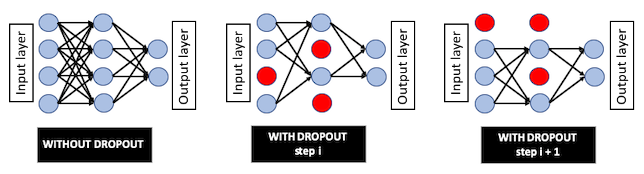
The following are the advantages of dropout: