December 2020
Intermediate to advanced
1064 pages
49h 43m
English
In the xy-plane, the length of an arc of the graph of y = f(x) from x = a to x = b is given by the definite integral
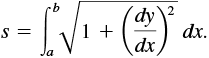 (1)
(1)
The problem in three dimensions, which is the counterpart of the arc length problem, is to find the area A(s) of that portion of the surface S given by a function z = f(x, y) having continuous first partial derivatives on a closed region R in the xy-plane. Such a surface is said to be smooth.
Suppose, as shown in FIGURE 9.13.1(a), that an inner partition P of R is formed using ...