8.9 CRIBBING OF STREAM ENCIPHERED ASCII PLAINTEXT
The stream encipherment of ASCII character plaintext is performed in three steps:
Step 1: Each letter of the character plaintext x0, x1, …, xn−1 is replaced by its ordinal value of xi in the ASCII character set, which is coded into 7 bits; for example
![]()
The ASCII character plaintext x0, x1, …, xn−1 of n characters is transformed into a sequence of n 7-bit vectors, the (0, 1)-plaintext
![]()
Step 2: The LFSR with initial state s(0) = (s0(0), s0(1), …, s0(N − 1)) generates the key stream, a sequence of 7n-bits (s0(0), s0(l), …, s0(7n − 1)), which are grouped into n 7-bit blocks:
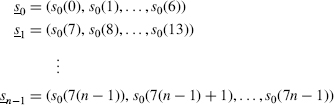
Step 3: The ciphertext y = (y0, y1, …, yn−1) consists of n 7-bit vectors where yi is the XOR of the ith plaintext block xi and the block of key si
![]()
The key of an LFSR encipherment system has three components:
- The number of stages N of the LFSR,
- The characteristic polynomial p(z) = cN + cN−1z + ··· + c1zN−1 + c0zN, and
- The initial state s(0) = (s0(0), s0(1), …, s0(N−1)).
We formulate the cribbing of ASCII character plaintext as:
| Given: | A plaintext crib ... |
Get Computer Security and Cryptography now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

