Bridge Domains
Wow. Who would have guessed that bridge domains would be so far down into the chapter? There was a lot of fundamental material that needed to be covered before encountering bridge domains. First, take a look at Figure 2-29.
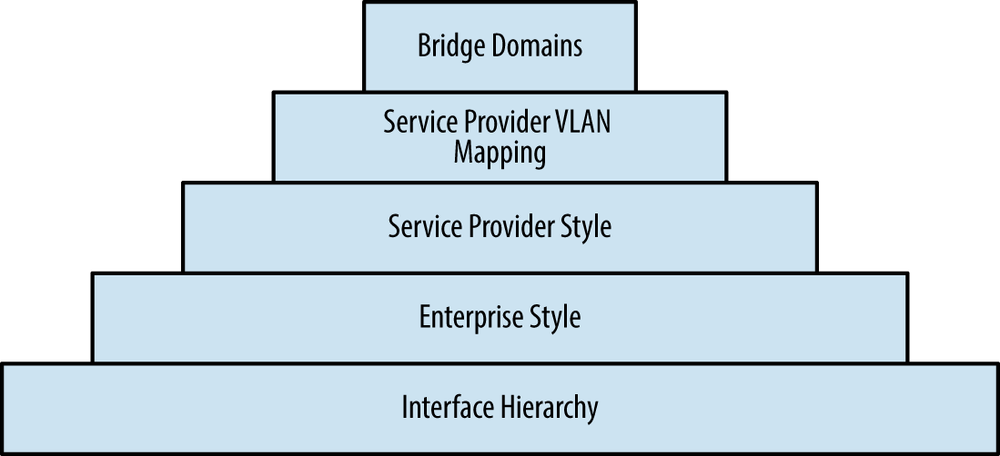
Figure 2-29. Learning hierarchy of Juniper MX bridging
Because the MX allows for advanced customization of bridging, it was best to start at the bottom and work up through interface hierarchy, configuration styles, and finally VLAN mapping.
Let’s get into it. What’s a bridge domain?
A bridge domain is simply a set of IFLs that share the same flooding, filtering, and forwarding characteristics. A bridge domain and broadcast domain are synonymous in definition and can be used interchangeably with each other.
Learning Domain
Bridge domains require a method to learn MAC addresses. This is done via a learning domain. A learning domain is simply a MAC forwarding database. Bridge domains by default have a single learning domain, but it’s possible to have multiple learning domains per bridge domain, as shown in Figure 2-30.
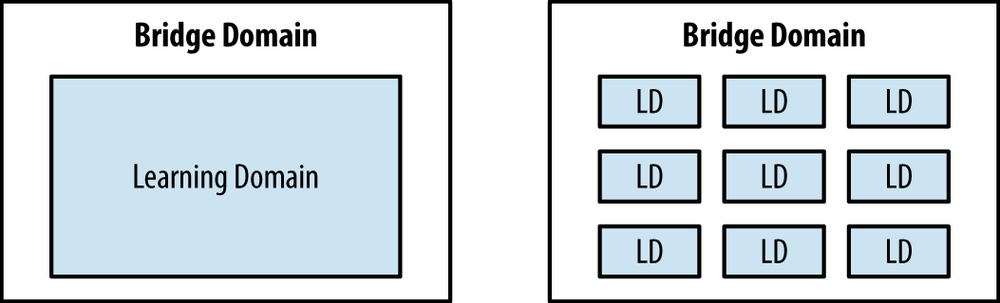
Figure 2-30. Illustration of Single Learning Domain and Multiple Learning Domains per Bridge Domain
Single Learning Domain
A single learning domain per bridge domain is the system default. When a bridge domain is configured with a single learning ...
Get Juniper MX Series now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

