Plugging in the Microsoft Index Server
Included with the freely available NT 4.0 Option Pack, the Microsoft Index Server is a powerful and feature-packed search tool. It’s also convenient, because it largely automates the indexing process. When installed, it registers with NT to receive filesystem change alerts and indexes on demand when the directories that it monitors change. That’s really helpful, especially for volatile docbases such as newsgroups that can acquire new content hourly. Even for archival docbases, it’s convenient not to have to do manual updates or to write scripts to automate scheduled updates. The simplest way to use Index Server is to mark your web server’s virtual root as indexable. To be more selective, turn off indexing at the root and enable it only for specific docbases. A docbase doesn’t have to reside in the web tree. If you define a virtual root for a docbase that you want to index, the corresponding physical path can be on any local or LAN-attached drive. Or you can specify a URL and use the indexer in web-spider mode. Figure 8.7 shows the setup for our analyst newsgroups.
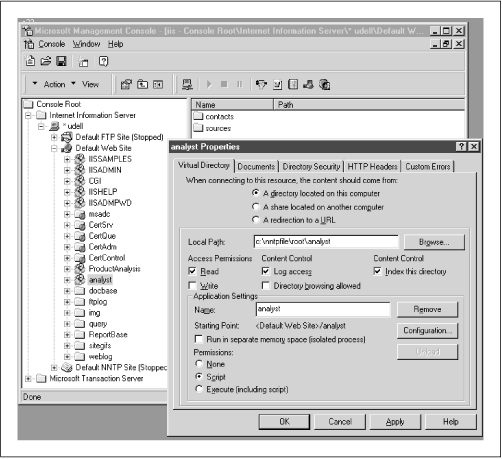
Figure 8-7. Index Server: Selecting a subtree for indexing
The virtual root /analyst maps to
the Microsoft NNTP spool directory
\nntpfile\root\analyst. If we set up another
root for the ProductAnalysis docbase, then run the indexer, the
Property pane in Index Server’s management ...
Get Practical Internet Groupware now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

