9.10 OBSERVABILITY
If any state of a system can not be observed from measurements, it is called unobservable. From Fig. 9.13, it is clear that the state x2 is not connected to output. Therefore the state x2 is called unobservable.
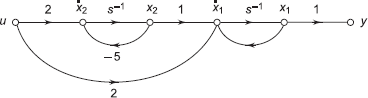
Fig. 9.13 x2 is unobservable
Any linear time invariant system can be represented by the dynamic equation
and y(t) = Cx(t) + Du(t)
The state x(t) is said to be observable if there exists a finite time t1 ≥ 0 for any given input u(t) so that the knowledge of u(t) for t1 ≥ t ≥ t0, the matrices A
Get Signals and Systems now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

