Synthesis of Arithmetic Circuits: FPGA, ASIC and Embedded Systems
by Jean-Pierre Deschamps, Gery J.A. Bioul, Gustavo D. Sutter
14.2 POLYNOMIAL COMPUTATION CIRCUITS
Polynomial approximation methods are often used to calculate special functions such as logarithmic, exponential, of trigonometric (Chapter 7). In Section 7.3.2 a recursive multilevel computation scheme was proposed as a generalization of the Hörner expansion technique to compute polynomials: the generalized Horner expansion (GHE). Using formulas (7.30)–(7.32), the example suggested in Section 7.3.2 is implemented in this section. The example consists of a 3-level GHE implementing a degree-63 polynomial to be computed in 9 multiply-and-add steps. First, 16 degree-3 polynomials can be computed (3 steps); then four degree-15 polynomials are worked out using the degree-3 polynomials as primitives (3 steps); another 3 steps are finally needed to compute the degree-63 polynomial using the degree-16 ones as primitives. The respective cells to be implemented correspond to the following polynomials:
First stage cells (Figure 14.14a)
![]()
Second stage cells (Figure 14.15a)
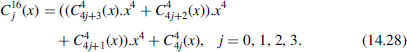

Figure 14.14 GHE degree-63 polynomial: first stage.

Figure 14.15 GHE degree-63 polynomial: ...