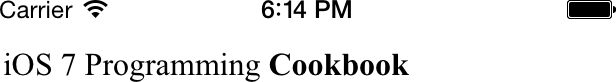A web view is what the Safari browser uses on iOS to load web
content. You have the whole power of Safari in your iOS apps through the
UIWebView class. All you have to do is place a web view on your UI and use one
of its loading methods:
loadData:MIMEType:textEncodingName:baseURL:loadHTMLString:baseURL:Loads an instance of
NSStringinto the web view. The string should be a valid HTML, or in other words, something that a web browser can render.loadRequest:Loads an instance of
NSURLRequest. This is useful when you want to load the contents of a remote URL into a web view inside your application.
Let’s see an example. We’ll start with the implementation file of our view controller:
#import "ViewController.h"@interfaceViewController()@property(nonatomic,strong)UIWebView*myWebView;@end@implementationViewController
Now I would like to load the string iOS 7 Programming
Cookbook into the web view. To prove, things are working
as expected and that our web view is capable of rendering rich text, I
will go ahead and make the Cookbook part bold
while leaving the rest of the text intact (Figure 1-65):
-(void)viewDidLoad{[superviewDidLoad];self.myWebView=[[UIWebViewalloc]initWithFrame:self.view.bounds];[self.viewaddSubview:self.myWebView];NSString*htmlString=@"<br/>iOS 7 Programming <strong>Cookbook</strong>";[self.myWebViewloadHTMLString:htmlStringbaseURL:nil];}
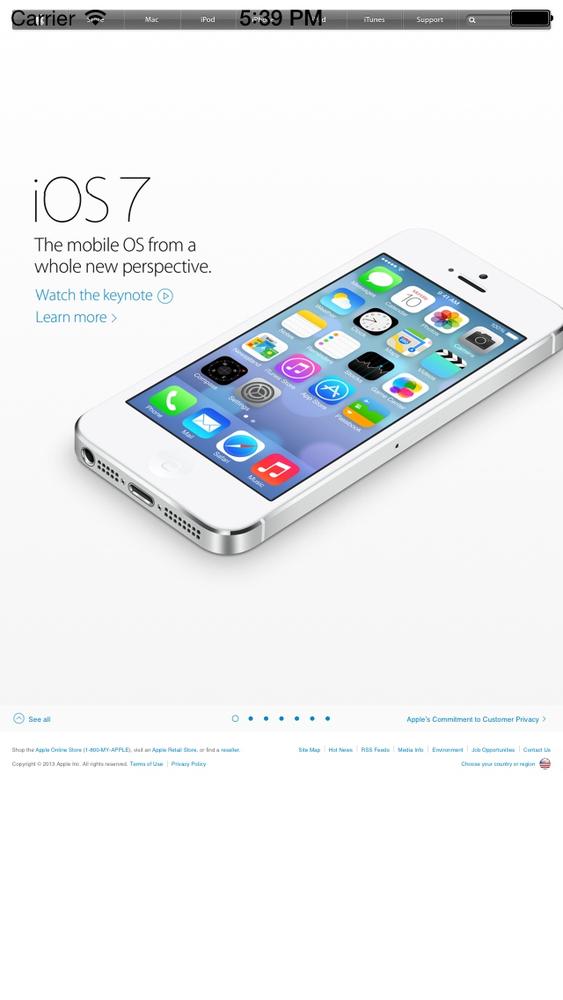
Another way to use a web view is to load a remote URL into it. For
this purpose, we can use the loadRequest: method. Let’s go ahead and look
at an example where we will load Apple’s main page into a web view in
our iOS app (Figure 1-66):
-(void)viewDidLoad{[superviewDidLoad];self.myWebView=[[UIWebViewalloc]initWithFrame:self.view.bounds];self.myWebView.scalesPageToFit=YES;[self.viewaddSubview:self.myWebView];NSURL*url=[NSURLURLWithString:@"http://www.apple.com"];NSURLRequest*request=[NSURLRequestrequestWithURL:url];[self.myWebViewloadRequest:request];}
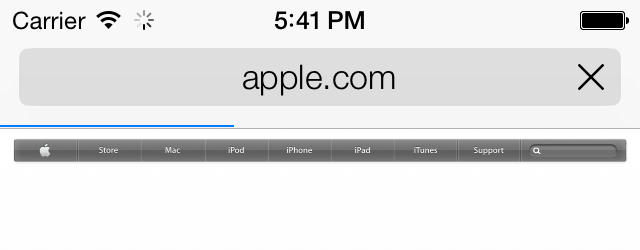
It might take quite a while for a web view to load the contents that you pass to it. You might have noticed that when loading content in Safari, you get a little activity indicator in the top-left corner of the screen telling you that the device is busy loading the contents. Figure 1-67 shows an example.
iOS accomplishes this through delegation. We will subscribe as
the delegate of a web view, and the web view will notify us when it
starts to load content. When the content is fully loaded, we get a
message from the web view informing us about this. We do this through
the delegate property of the web
view. A delegate of a web view must conform to the UIWebViewDelegate protocol.
Let’s go ahead and implement the little activity indicator in our
view controller. Please bear in mind that the activity indicator is already a part
of the application and we don’t have to create it. We can control it using the setNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible: method of
UIApplication. So let’s start with
the implementation file of our view controller:
@interfaceViewController()<UIWebViewDelegate>@property(nonatomic,strong)UIWebView*myWebView;@end@implementationViewController
Then do the implementation. Here we will use three of the methods
declared in the UIWebViewDelegate
protocol:
webViewDidStartLoad:This method gets called as soon as the web view starts loading content.
webViewDidFinishLoad:This method gets called as soon as the web view finishes loading content.
webView:didFailLoadWithError:This method gets called when the web view stops loading content, for instance because of an error or a broken network connection.
-(void)webViewDidStartLoad:(UIWebView*)webView{[[UIApplicationsharedApplication]setNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible:YES];}-(void)webViewDidFinishLoad:(UIWebView*)webView{[[UIApplicationsharedApplication]setNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible:NO];}-(void)webView:(UIWebView*)webViewdidFailLoadWithError:(NSError*)error{[[UIApplicationsharedApplication]setNetworkActivityIndicatorVisible:NO];}-(void)viewDidLoad{[superviewDidLoad];self.myWebView=[[UIWebViewalloc]initWithFrame:self.view.bounds];self.myWebView.delegate=self;self.myWebView.scalesPageToFit=YES;[self.viewaddSubview:self.myWebView];NSURL*url=[NSURLURLWithString:@"http://www.apple.com"];NSURLRequest*request=[NSURLRequestrequestWithURL:url];[self.myWebViewloadRequest:request];}
Get iOS 7 Programming Cookbook now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.