3.1 INTRODUCTION
Pipelining transformation leads to a reduction in the critical path, which can be exploited to either increase the clock speed or sample speed or to reduce power consumption at same speed. In parallel processing, multiple outputs are computed in parallel in a clock period. Therefore, the effective sampling speed is increased by the level of parallelism. Similar to the pipelining, parallel processing can also be used for reduction of power consumption.
Consider the three-tap finite impulse response (FIR) digital filter
![]()
The block diagram implementation of this filter is shown in Fig. 3.1. The
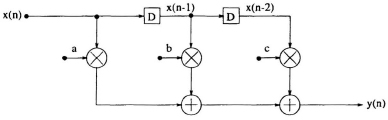
Fig. 3.1 A 3-tap FIR filter.
critical path or the minimum time required for processing a new sample is limited by 1 multiply and 2 add times, i.e., if TM is the time taken for multiplication and TA is time needed for addition operation then the “sample period” (Tsample) is given by,
![]()
Therefore, the sampling frequency (fsample) (also referred to as the throughput or the iteration rate) is given by
![]()
Note that the direct-form structure shown in Fig. 3.1 can only be used when ( ...
Get VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

