December 2018
Beginner to intermediate
684 pages
21h 9m
English
An increase in the number of dimensions of a dataset means there are more entries in the vector of features that represents each observation in the corresponding Euclidean space. We measure the distance in a vector space using Euclidean distance, also known as the L2 norm, which we applied to the vector of linear regression coefficients to train a regularized Ridge Regression model.
The Euclidean distance between two n-dimensional vectors with Cartesian coordinates p = (p1, p2, ..., pn) and q = (q1, q2, ..., qn) is computed using the familiar formula developed by Pythagoras:
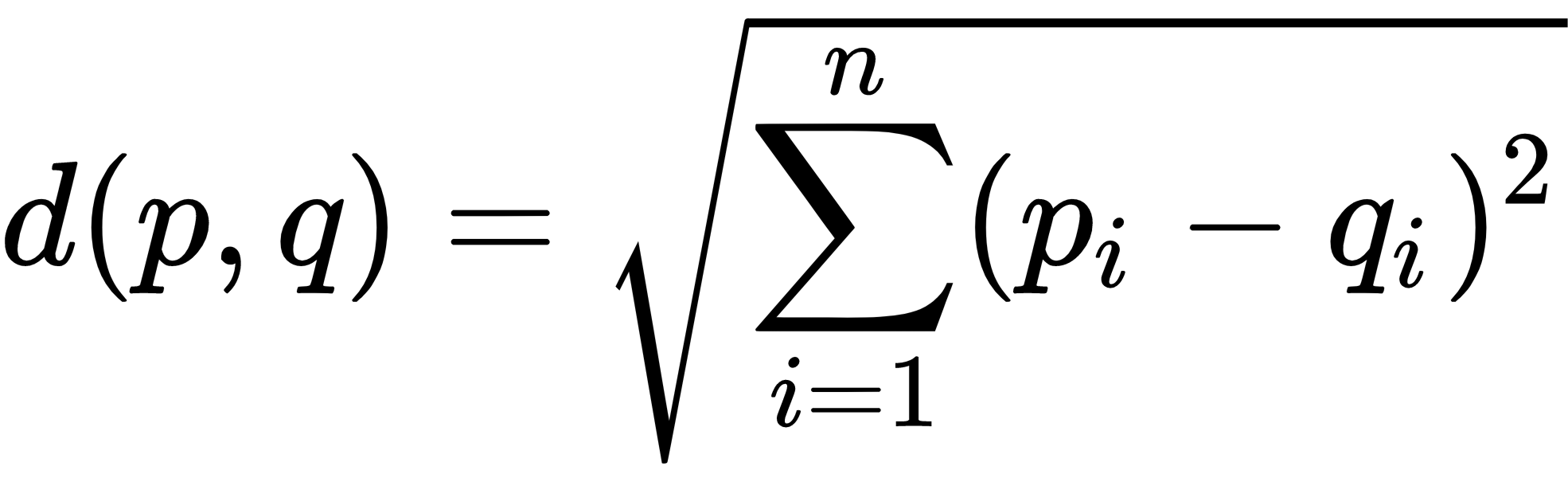
Hence, each new dimension adds a non-negative ...