December 2018
Beginner to intermediate
684 pages
21h 9m
English
The Q-learning algorithm keeps improving a state-action value function after random initialization for a given number of episodes. At each time step, it chooses an action based on an ε-greedy policy, and uses a learning rate, α, to update the value function, as follows:
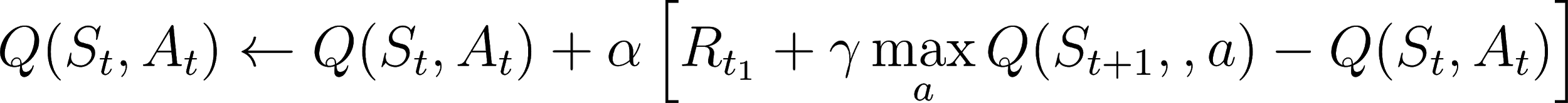
Note that the algorithm does not compute expected values because it does know the transition probabilities. It learns the Q function from the rewards produced by the ε-greedy policy and its current estimate of the value function for the next state.
The use of the estimated value function to improve this estimate is called bootstrapping. The Q-learning ...