4.7
ヒストグラム、ビニング、密度
249
plt.hist
の
docstring
には、その他のカスタマイズオプションが数多く解説されています。異
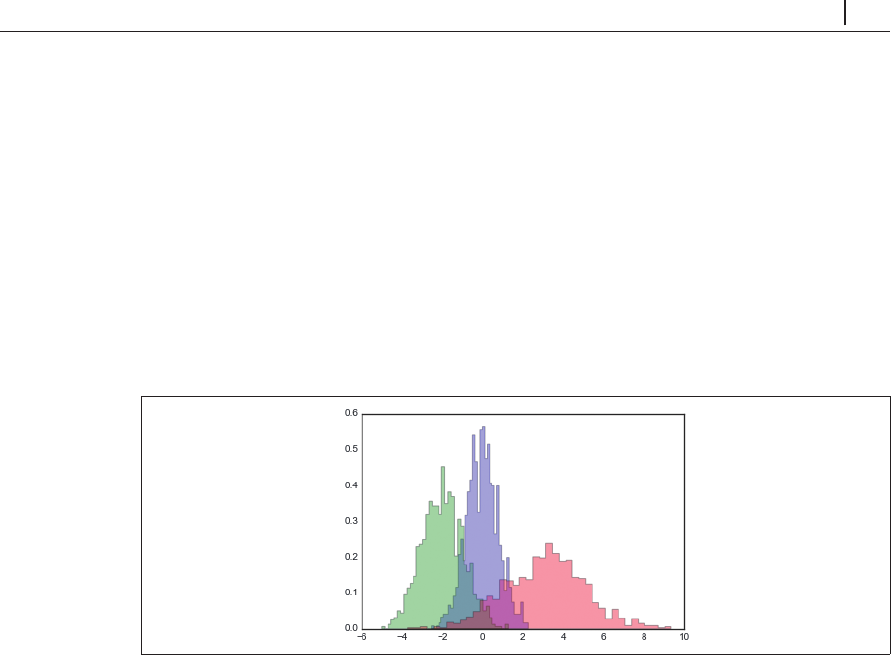
なる分布のヒストグラムを比較する際には、
histtype='stepfilled'
オプションを使い、透過度
alpha
を設定すると見やすいグラフになります(図 4-37)。
In[4]: x1 = np.random.normal(0, 0.8, 1000)
x2 = np.random.normal(-2, 1, 1000)
x3 = np.random.normal(3, 2, 1000)
kwargs = dict(histtype='stepfilled', alpha=0.3, normed=True, bins=40)
plt.hist(x1, **kwargs)
plt.hist(x2,
**kwargs)
plt.hist(x3, **kwargs)
図4-37 ヒストグラム重ね合わせ
単にヒストグラムの計算だけを行い(つまり、指定されたビン内のポイントの数を数えて)、そ
れを表示しないのであれば、
np.histogram()
関数が利用できます。
In[5]: counts, bin_edges = np.histogram(data, bins=5)
print(counts)
[ 12 190 468 301 29]
4.7.1
2
次元のヒストグラムとビニング
データ列をビンに分割して
1
次元のヒストグラムを作成するのと同様に、
2
次元
