448
5
章 機械学習
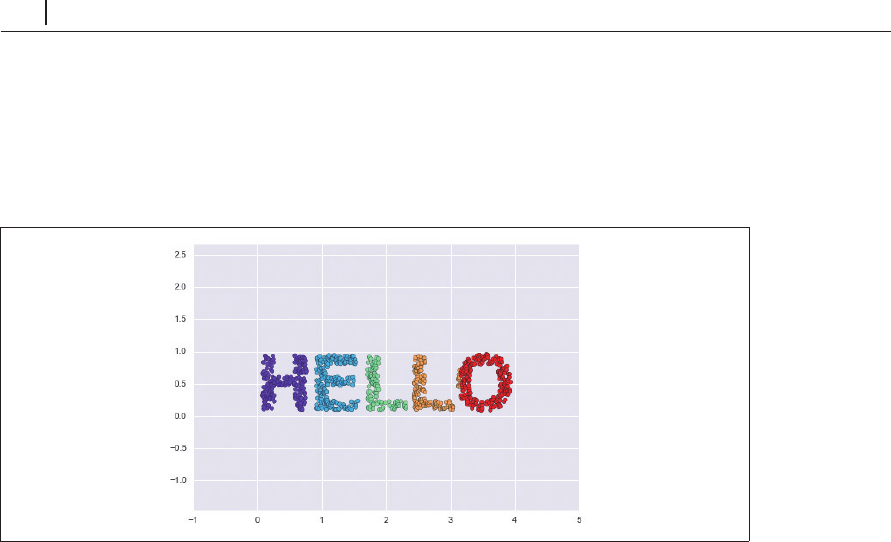
この関数を呼び出し、結果を可視化します(図 5-94)。
In[3]: X = make_hello(1000)
colorize = dict(c=X[:, 0], cmap=plt.cm.get_cmap('rainbow', 5))
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], **colorize)
plt.axis('equal');
図5-94 多様体学習に使用するデータ
2
次元の出力は、「
HELLO
」の形をしています。このデータにより、それぞれのアルゴリズムの
働きが視覚的に把握しやすくなります。
5.10.2
多次元尺度構成法
このようなデータを見ると、
x
値と
y
値はデータの最も基本的な記述方法ではないことがわかり
ます。データを拡大、縮小、回転を行っても、データは「
HELLO
」に見えます。例えば、回転行列
を使用してデータを回転すると
x
と
y
の値は変化しますが、データそのものは基本的に変わりませ
ん(図 5-95)。
In[4]: def rotate(X, angle):
theta = np.deg2rad(angle)
R = [[np.cos(theta), np.sin(theta)],
[-np.sin(theta), np.cos(theta)]]
return np.dot(X, R)
X2 = rotate(X, 20) + 5
plt.scatter(X2[:, 0], X2[:, 1], **colorize)
plt.axis('equal'); ...
