2.9
構造化データ:
NumPy
の構造化配列
95
型の名前が重要でないなら、カンマ区切りの文字列で型だけを指定できます。
In[13]: np.dtype('S10,i4,f8')
Out[13]: dtype([('f0', 'S10'), ('f1', '<i4'), ('f2', '<f8')])
短縮された文字列形式の型コードは複雑に見えますが、単純な原則に基づいています。最初の(省
略可能な)文字は、それぞれ「リトルエンディアン」または「ビッグエンディアン」を意味する
<
また
は
>
であり、最上位ビットの位置を指定します。次の文字は、データの種類(文字、バイト、整数、
浮動小数点など)を表します(表2-4を参照)。最後に、バイト単位のオブジェクトのサイズを指定
します。
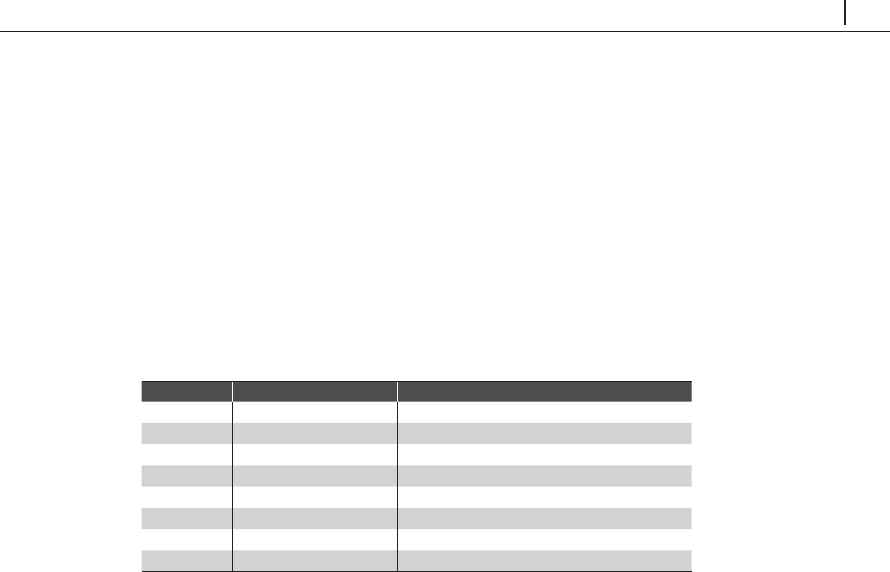
表2-4 NumPyのデータ型
文字 説明 例
'b'
バイト
np.dtype('b')
'i'
符号付き整数
np.dtype('i4') == np.int32
'u'
符号なし整数
np.dtype('u1') == np.uint8
'f'
浮動小数点数
np.dtype('f8') == np.int64
'c'
複素数
np.dtype('c16') == np.complex128
'S'
,
'a'
文字列
np.dtype('S5')
'U'
Unicode
文字列
np.dtype('U') == np.str_
'V'
Raw
データ(
void
)
np.dtype('V') == np.void
2.9.2
より高度な複合型
より高度な複合型を定義できます。例えば、各要素が配列や行列である型を作成できます。ここ ...
